FGP
Overview
The FGP programme is a shift from direct input subsidy to a smart agricultural Input Credit System, linked to structured market arrangements. The programme will be implemented over a period of five years and will adopt an integrated and comprehensive approach to increase the availability and access to improved inputs, mechanization and extension services as well as output markets.
The programme is anchored on four main principles:
- Value chains
- Private sector focus
- Market driven and
- Inclusivity
Under FGP, eleven commodities have been prioritized for promotion and development of the agricultural sector.
The commodities are:
- Grains (maize, rice, soybean, sorghum);
- Vegetables (tomato, pepper, onion);
- Roots and tubers (cassava, yam); and plantain
- Poultry (broilers)
Goal and Objectives
The overall goal of the FGP programme is to transform and modernize agriculture in Ghana through the development of selected agricultural value chains with active private-sector participation. The programme has six interrelated specific objectives:
- Ensure food availability: By supporting the production of 11 prioritised commodities.
- Reduce food price inflation: Through increased production and improved storage and reduction in post-production wastage.
- Promote import substitution: By increasing production and processing of selected import substituted crops.
- Promote exports: By supporting the production of selected crops with export potential and ensuring that they meet the required standards.
- Create jobs: Lends itself to creation of jobs along the entire commodity value chains and providing employment and growth opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises in the agricultural sector.
- Ensure food security and resilience: By promoting sustainable agricultural practices and ensuring that the country's food supply is not only sufficient but also resilient in the face of shocks such as natural disasters or pandemics.
Elements/features
The FGP has five key elements namely:
- An input credit system
- High-quality inputs and other support services
- Storage Infrastructure
- Off-taker arrangements
- Digitized Platform for management
- Monitoring and coordination.
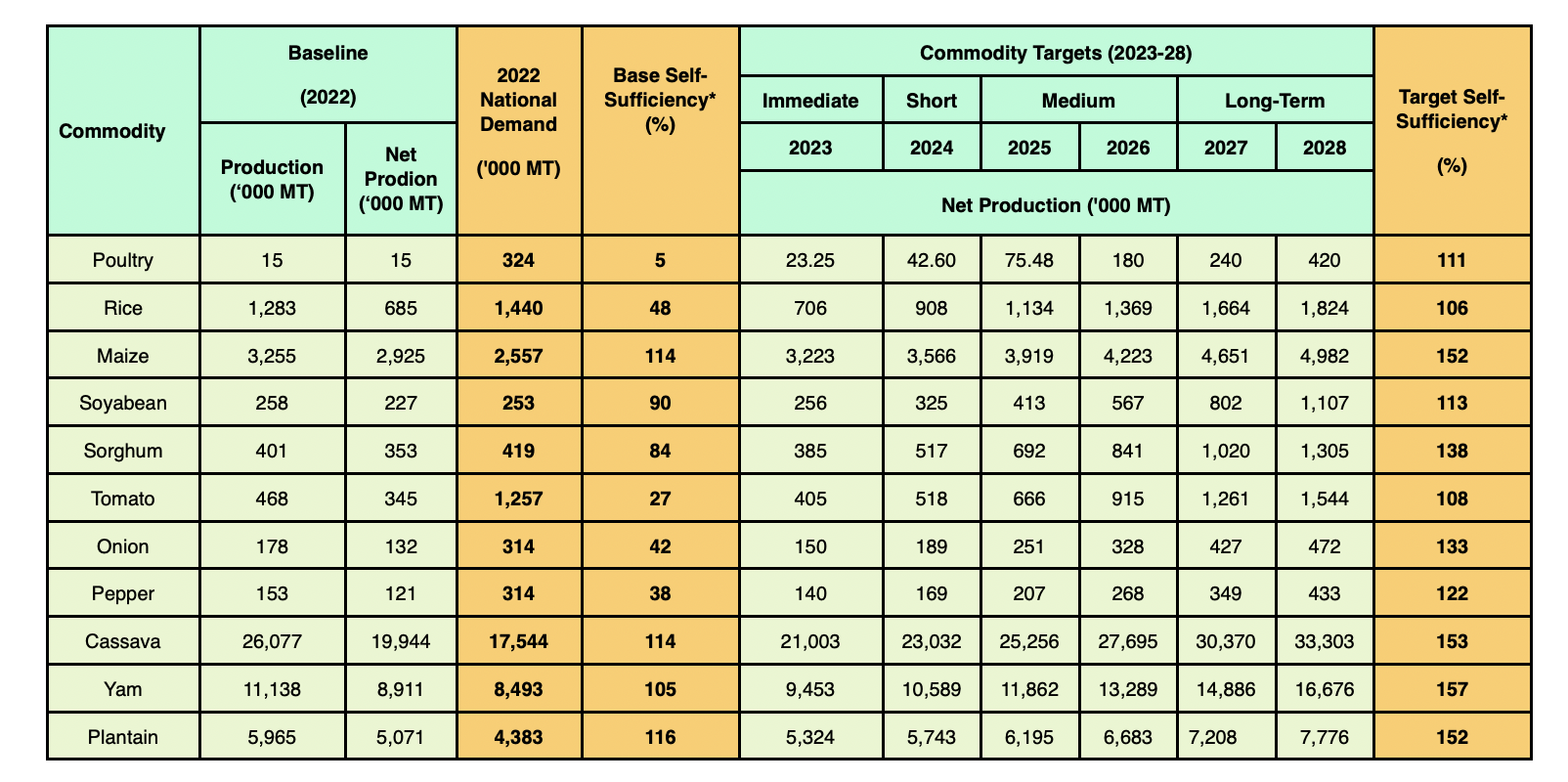
Target
Targeted Production Levels of Priority Commodities
Interventions
The major interventions under the FGP include:
-
Development of agricultural zones for expanded commodity production.
Agricultural Zones are being established under FGP to serve to address the issue of access to large tracts of agriculture land and drive sustainable and commercially oriented agriculture. The aim is to significantly expand the productive capacity in food commodities such as rice, poultry, maize, and tomato. Each zone is ccontiguous tract of arable land of not less than 300 hectares designed and developed as an integrated precinct, within which a modern agricultural economic enclave will be located. - Provision of improved inputs - seeds, quality fertilizers, improved breeds as input credit, The FGP engages input suppliers to provide the requisite agricultural inputs including certified seeds, high-quality fertilizers, vaccines, day-old chicks, feed, agro-chemicals etc. to registered farmers as input credit to be paid back at the end of production.
- Provision of quality services- mechanization, irrigation and extension services as service credit Under the FGP programme, service providers including mechanization, irrigation and agricultural extension service providers are engaged to provide services to farmers for increased crop production and productivity.
-
Provision of markets opportunities.
Access to markets is improved under FGP with farmers being liked to aggregators to purchase farmers’ produce as a first option.
